To an organization to be successful in the current competitive world and with highly competitive industrial norms, it should be able to sustain in the market with a continual growth and meanwhile increase their profits to run the business smoothly and to develop itself. Nowadays with the high inflation, all the general public try to reduce their expenses hence this make all businesses to control the market prices of their products or services in spite of the thriving prices of resources, raw materials and over heads.
With many competitors in the market for the same product or
service, it is almost impossible to make profits with just increasing the sales
prices. To increase profits of a business, the company shall improve their
sales pitches, increase or maintain the good quality of the product or service,
reduce operational costs, improve delivery methods and options, and take more
actions to make profits meanwhile being sustained in the business.
TPM is now a blooming concept in the industrial world with
various concepts come in to one system to improve the productivity,
efficiencies and other profitable factors of an organization.
(Nakajima, 1988) the father of TPM considered this as
“profitable TPM” as reducing the cost of maintenance delivers automated increment
in profits. (Yamashina, 2000) Concluded that TPM could be a principal source of
profitability of a manufacturing organization.
TPM technically abbreviated as “Total Productive Maintenance” or “Total Productivity Management”. But with the work carried out in
the TPM concept finally give an organization a considerable increase in their
profits as this will reduce all types of operational costs and operational
losses by a considerable fraction including, sales, marketing, repair and
maintenance, downtimes, defects and rework, consumables, motions, logistics,
etc.
There are 3 major resultants which could be gained upon
successful implementation of TPM, which are “Zero Breakdowns”, “Zero
Defects” and “Zero Accidents”.
A general definition of TPM is “carrying out maintenance at the optimum cost”. An organization shall
carry out its maintenance at zero cost, a.k.a. does not carry out any
maintenance. And also, an organization may carry out its maintenance at any
cost a.k.a. carry out maintenance activities which are not required and which
are not with the machine manufacturer stated guidelines.
Both the systems will make the organization loose a huge sum
of money at the end as both those methods will fail the machinery at the end
or waste money which should not be expended.
Therefore, with the proper implementation of TPM concept in
failure prevention and machine maintenance activities, wasting of money can be
totally eliminated.
In TPM, a repair or a maintenance activity of a machine should
be carried out while the machine is at its running condition and or with the
shortest downtime possible. These are addressed in the “Planned Maintenance Pillar” which is one of the eight pillars of
TPM and which is an essential pillar. In Planned maintenance, all
deteriorations are identified and the most appropriate maintenance method for
each deterioration method is identified. The maintenance activities are
segregated in to two parts which one will sustain the best possible condition
of the machine and the other will improve the machine with kaizens.
All these maintenance activities done at the right time, with
right materials and equipment and with right expertise will reduce all types of
issues of the machines, resulting less or zero downtimes. Also, it will
eliminate any type of chronic losses and reduce the possibilities of creating
any sporadic losses in the machines.
These methods will also create space for programmable management
of the stocks of spare parts of machinery as the planned maintenance can
predict the spare part requirements and also will reduce the spare parts
consumptions.
Finally, proper planned maintenance will assist to create an
environment with “Zero Breakdowns”,
“Zero Defects” and “Zero Accidents” which are the 3 major
resultants of TPM. A planned maintenance will reduce any abnormal and
exceptional costs of machine repairs and maintenances with relate to spare
parts, man hours, machine availability, defective production and also any kind
of accidents which will directly affect the operational cost of the production
process.
There is another
indicator which is used to define the effects of TPM in a production process
which is in short named as “PQCDSM”
which denotes the words Productivity, Quality, Cost, Delivery, Safety and
Morale of a system.
TPM methodology is a very effective strategy for improving productivity and overall plant
efficiency. The lost production output due to material productivity, manpower
productivity, and tools productivity will be reduced and there will be a 1.5 to
3 times increment of OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) and/or productivity
with TPM implementations. All losses
from the 16 losses which affect productivity are answered in TPM implementation
and with the elimination of those losses, the productivity and efficiency of a
system will improve which will give many ways of financial benefits to an
organization.
Quality has been considered as one of the utmost capable parameters
for creating the brand image. To make the product a “good quality product”, the
product must cater the customer requirement and should not have any kinds of
defects where the defect may cause the product to not to cater the customer
requirement during the indented operations.
(Feigenbaum, 1991) have clearly indicated that a TPM programme
can result in better product quality, improved manufacturing flow, and
reduction in operational expenses & losses, etc. TPM also aims at continual
and lifelong improvements in productivity & performance and therefore it
results in improving the monetary output of an organization in terms of market
segment and profits.
Therefore, to improve the quality of the product and reach
zero customer complaints and reworks, the product shall be with Zero Defects.
This can be done by eliminating rejection/rework, by avoiding mistakes in the
preparation of product, machines, methods, man power and also documentations.
In broader times, it means by meeting customer expectations so that there
should be no return of customer in any means. Customer complaints can be
reduced significantly and ultimately reach zero after the implementation of TPM
initiatives.
The “Quality
Maintenance Pillar” in TPM acts as the major constituent to control the
quality of the product with various control points in the processes, by
identifying the Quality components of each and every machine and their effects
to the product quality, etc. will create the requirement of fulfilling
countermeasures for identified issues related to deteriorations, cleaning,
lubrication, inspection, tightening, and repairing the machine and parts which
may create problems to the machine and the production process. Quality
Maintenance Pillar will decide the countermeasures which should be taken to
answer all issues and give required training to the machine operatives and
technicians to eliminate issues which could be created with each Q component.
Therefore, as stated before, improving not only the quality of
the product, but also quality of other 3Ms which are Man, Materials and
Machines will directly affect the revenue of the company hence increase the
profitability of the organization.
TPM has been a very fruitful in terms of improving operational
performance of organizations. TPM claims to have an optimistic influence on cost indicator as per (Feigenbaum, 1991).
It is because all eight big losses are monitored thoroughly to improve the OEE
and this expressively increases the manufacturing yield within the same time interval.
Also, the average operational cost will come down with higher manufacturing
yield with the same inputs.
There are many costs involved in a product which finally
decide the production unit cost and the sales price of a product, which
ultimately decide the profit created from the product. TPM concept helps to
reduce the manufacturing cost by 30% to 50% through reducing operational and
maintenance cost, inventory carrying cost and cost of communication, etc.
Delay or imprecise deliveries
will have a negative impact on customer satisfaction and also the organization’s
brand image. CCFOT (Customer Cases
Fill On Time) or the Fill Rate is a
parameter which the customers look for in a good product, secondly to the price
and quality. To make the customers happy and content, they need a precise,
faster and a timely delivery method
of any product.
There can be various reasons for the delivery delays such as delay
in production processes, supplier inconsistencies, delay in payments to
suppliers, delay in packing, delay in procurement process, delay in information
transfers, which ultimately cause the delays in logistics and then the final
delivery. Other than those, external delays like customs formalities, government
inspections, and system failures can also affect the on-time delivery.
TPM helps to deliver 100% goods on time to the customer. It
can be achieved by minimizing the delays in production processes, logistic activities,
delivery methods, and any of the support functions as stated above. A proper
delivery is an activity which will increase the customer satisfaction and hence
increase the loyalty of the customers.
There are several losses defined in TPM 16 losses structure
which will affect the delays in delivery. They are breakdown losses, adjustment
losses, quality and defects losses, yield losses, management losses, logistics
losses and line organization losses. Eliminating these losses will create an in-time
production output hence eliminate delays in product deliveries.
Product inventory is also an additional cost to an
organization in relate to maintaining the stocks in good conditions, the stores
space consumed by the inventories and the depreciation of goods. TPM will be
able to reduce the product inventory at least by 50% which will reduce the
operational costs relate to product inventory handling which will also improve
the delivery which reduce the costs incur.
Safety is one of the major factors considered in TPM with targeting
a Zero Accidents environment inside an organization. TPM concept will create an
accident-free zone area by ensuring safety while working on machines, safety in
material handling, safety in packaging, safety in transportation, and safety in
almost everything.
Inside an organization, the 4Ms which are Man, machines,
Methods and Materials are contributing to the safety of the activities, health
of the humans and pollution of the environment. Almost all the accidents happen
due to unsafe acts and unsafe conditions of humans and activities. Incorrect workplace
designs, operator’s carelessness, unsuitable design of the equipment and tools,
damaged utensils, lack of effective protection guards for equipment, lack of
fire preventive systems, hostile working conditions such as high noise and air
pollution are some of the instances for unsafe acts and unsafe conditions.
The element Man is the most complicated factor in maintaining
safety and wellbeing in an organization. The equipment and materials can be
made safer to a favorable extent with various controls like safety sensors, Poka
Yoke, safety SOPs (Standard Operational Procedures) or Guidelines. The human aspect
must be mainly supposed in the incident and accident prevention.
Training will be done in the TPM implementation related to
safety, health, operational knowledge, etc simultaneously along with the other
training while moving towards Zero accidents concept. Fundamental principles of
TPM include guaranteeing equipment reliability, maintainability, preventing
human and eliminating accidents and environmental pollution.
Therefore, when the Safety and good health of the organization
and the people inside are considered, “Safety,
Health and Environment Pillar” in TPM
8 pillars structure plays the
major role in keeping the level of safety. In the SHE pillar, all hazards
related to occupational safety & health and aspects related to
environmental pollution are identified and counter actions are taken to
eliminate or reduce them. Safety related trainings are planned and carried out
to all employees within the organization through the SHE pillar activities and
ensure that all employees are knowledgeable in safety protocols in the
organization and all the employees carry out their work according to the given
SOPs and safety instructions.
The ultimate outcome of those activities will be zero
environment, safety and health related incidents / accidents which will eliminate
or reduce any costs incur for solving issues related to environmental impacts
and compensating for accidents occurred inside the organization or any health
issues created during the activities in the organization which will reduce the
company expenses at the end.
A successful organization will increase the morale of employees which will boost up
the organizational activities. TPM helps to boost up the employees of the
organization by making them participate in contributing a number of kaizens,
one-point lesson (OPL). The increased morale of employees will increase the
number of improvement suggestions by employees them selves by 5 to 10 times.
If the employees are extremely motivated and contented with
the work culture, they are more productive and engaged. If they are not
motivated, there is a more tendency of they are being less productive in the
organization. For inspiration and preserving the enthusiasm with optimistic
focus over the period, morale is an important TPM indicator.
Laying banners, publishing TPM newsletters, posting TPM
posters at specified locations, designing TPM slogans and displaying them can
create a constructive atmosphere and encourage employees to create a healthy
workforce culture. To improve the morale of the employees, giving motivation
awards to contributing employees in organizational events or meetings can be
carried out. The increased morale of employees will create a much better
results in production processes and improvement suggestions hence increase the
profitability of the organization as employees tends to work better and give
better results.
It is very important to measure and understand the method of
measurements of losses in the manufacturing process (Eswaramurthi,
2013). Losses can be divided into two categories named as “chronic losses and sporadic losses”.
Chronic losses
are usually small, hard to identify and complicated since they are results of
several simultaneous causes. Sporadic losses are more noticeable since the
deviations from the normal state are large.
Sporadic
losses occur irregularly and their effects are considered to lead to serious
problems with regard to large downtimes, high percentage of defects and maybe
also accidents. But there are chronic losses that result in the equipment frequently
but with smaller deviations from the normal state. With the time, those maybe
considered as normal and maybe neglected also. Although they are small, they
make large costs due to the fact that they occur repeatedly and continuously.
The
calculation of OEE can identify these losses whereby can be used to find
solutions for those losses hence reduce the operational costs. The major
contributing eight losses in the 16 losses structure can be identified in the
OEE calculation and all related chronic and sporadic losses should be answered
giving solutions to them with the TPM initiatives. This will increase the
productivity, efficiency and quality of the production process hence affect the
PQCDSM in a positive manner where again gives various kinds of financial gains
to the organization.
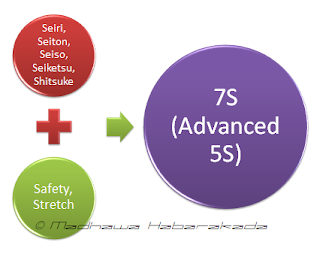
The whole concept of TPM structure is based upon the 5S principle where TPM defines a new
concept of 7S principle. Other than
the Seiri (Sort), Seiton (Set Locations), Seiso (Shine), Seiketsu (Standardize)
and Shitsuke (sustain), 7S is giving additional provisions to Safety and
Stretch (Improvements). The traditional
5S principle again have developed in to “Advanced
5S principle” where the final objective becomes profit, not
discipline.
The advanced 5S principle is supporting all the concepts of
TPM and nevertheless advanced 5S can cater the requirements of TQM (Total
Quality Management) and Lean (waste minimization) also. It is a cultural
changing tool and a standardizing tool which can target threes zeros defined in
TPM which are zero breakdowns, zero defects and zero accidents. it also can directly
involve to improve the PQCDSM in an organization. This will also give an
effective solution to the elimination of seven wastes which are excess
transportation, excess inventory, useless motions, higher waiting time, over
production, over processing and defective products. All these wastes are
financially loose points and elimination of those will reduce the costs of an
organization in a considerable way.
5S can make an organization a safe place and create work
friendly working environment. With the elimination of 4Ds (Danger, Dark, Dirty
and Difficulties), a workplace become safe to work with less cluttered
environment and with less ergonomic issues. It will assist to achieve zero
accidents and will improve the safety and morale of the employees. These two
achievements will affect the productivity of the employees hence reduce any
costs which may arise from unsafe work activities and accidents.
Elimination of useless things such as broken and unusable
machines, expired or unwanted materials, obsolete documents will eliminate the
risks of accidents relate to human safety, machine safety and process safety.
Also, unwanted things will take up warehouse space which is also a cost and
will be reduced with elimination of those expenses.
When the machines are clean enough and the level of cleaning is
maintained, the problems of the machines can be easily identified and any
improvements, modifications, corrections can be easily done. This will assist
the zero-breakdown concept and furthermore, this will reduce any deteriorations
hence reduce the costs for repairs and spare parts.
With implementation of visual management tools and visual
controls with 5S, the organization becomes much neat and tidy. The activities
which are carried out inside the organization would be much efficient and fast.
For instance, with the visual controls, all abnormalities in all activities can
be easily seen and identified where corrective/preventive actions could be
taken in advance without causing any adverse events to product, machine or
humans.
With the advanced 5S, people are motivated to give suggestions
for improvements and kaizens through the suggestions for improvements system.
The kaizens or suggestions will assist to improve the productivity or
efficiency of the processes and machineries. Also, the suggestions will answer
any kinds of sporadic or chronic losses inside the organization’s production
processes. Upon implementation of these kaizen suggestions, the OEE of the
processes will be increased creating a profitable condition for the
organization.
5s can maximize the profits and increase sustainability of an
organization by taking initiatives to enhance the productivity and efficiency.
Each and every company spend huge sum for giving training for their employees. In-house,
external, local, foreign training is given to employees to improve their
skills, capabilities, professional experience, etc. But in most cases those trainings are not effective and
do not improve the organization's profitability. (Habarakada, 2018)
There are various reasons which employers raise regarding the training they give to their employees. Training is being used as a motivational tool and in some cases, employers want to improve the employee profiles of the organization. There are companies who give generic training to their employees without selecting the suitable set of people for a specific training. The correct skills gaps are not identified by employers and the trainings are given blindly to selected employees irrespective of the requirements. (Habarakada, 2018)
There are various reasons which employers raise regarding the training they give to their employees. Training is being used as a motivational tool and in some cases, employers want to improve the employee profiles of the organization. There are companies who give generic training to their employees without selecting the suitable set of people for a specific training. The correct skills gaps are not identified by employers and the trainings are given blindly to selected employees irrespective of the requirements. (Habarakada, 2018)
With the TPM initiatives, the training will be highly targeted
and the required training will be given to the required employees only. The
skills gaps will be identified individually and the identified gap will be
filled with giving required and targeted trainings.
The internationally know ETHOS
process would be carried out on selection & identification, training and
evaluation of deliverables on trainings.
The correct training needs required inside the organization is
identified with the Loss Tree analysis and then with 4M analysis. Skill gaps of
each and every employee is identified via a detailed skills matrix evaluation
and a training needs identification system. The identified skill gap will be
answered by the training given to the employee. And finally, the employee will
be given target/project/KPI to improve, with the learnings he / she received.
This will improve the organization’s OEE and KPIs which will result in
reductions of costs, improvements in productivity and efficiency, etc.
With these all stated points, it is certain that TPM
implementation will improve the productivity and efficiency of machines and
processes, reduce all kinds of wastes in an organization, reduce costs of each
and every process, etc.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the TPM concept will
increase the profitability of an organization and hence, TPM can also be
defined as “Total Profit Management”.
There are only few points were discussed here considering the above finally stated fact, and this can be continued further giving much more reasons establishing the phrase "TPM stands for Total Profit Management".
REFERENCES
Nakajima, S. (1988)
Introduction to TPM: Total Productive Maintenance (preventative maintenance
series).
Yamashina, H. (2000)
Challenge to world‐class manufacturing, International Journal of Quality &
Reliability Management, Vol. 17 Issue: 2
Feigenbaum, A.V. (1991) Quality Control. 3rd Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Eswaramurthi, K.G. (2013)
Improvement of manufacturing performance measurement system and evaluation of
overall resource effectiveness, American Journal of Applied Sciences.
Habarakada,
M. (2018) “Training is a Waste.
WHY?”, http://www.engineermadhawa.tk/2018/06/training-is-waste-why.html
TPM stands for Total Profit Management by MadhawaHabarakada is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at http://engineermadhawa.blogspot.com/.
Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at http://engineermadhawa.blogspot.com/p/contact.html.
©
All rights reserved. 2018.07.16.
Unauthorized
copying and redistribution is prohibited. Proper Attribution should be given, provide
a link
to the license, and indicate if changes were made when adopting content of this
article.
By, Eng. Madhawa Habarakada. (AMIE-SL, BSc. Eng. (Hons))
http://engineermadhawa.blogspot.com/
Your comments are welcome.










No comments:
Post a Comment
Your ideas and inquiries are always welcome.